CVE-2025-32756: Zero-Day Vulnerability in Multiple Fortinet Products Exploited in the Wild

Fortinet has observed threat actors exploiting CVE-2025-32756, a critical zero-day arbitrary code execution vulnerability which affects multiple Fortinet products including FortiVoice, FortiMail, FortiNDR, FortiRecorder and FortiCamera.
Background
On May 13th, Fortinet published a security advisory (FG-IR-25-254) for CVE-2025-32756, a critical arbitrary code execution vulnerability affecting multiple Fortinet products.
| CVE | Description | CVSSv3 |
|---|---|---|
| CVE-2025-32756 | An arbitrary code execution vulnerability in FortiVoice, FortiMail, FortiNDR, FortiRecorder and FortiCamera | 9.6 |
Analysis
CVE-2025-32756 is an arbitrary code execution vulnerability affecting multiple Fortinet products including FortiVoice, FortiMail, FortiNDR, FortiRecorder and FortiCamera. A remote unauthenticated attacker can send crafted HTTP requests in order to create a stack-based overflow condition which would allow for the execution of arbitrary code. This vulnerability was discovered by the Fortinet Product Security Team who observed threat activity involving a device running FortiVoice.
According to Fortinet, the threat actors operations included scanning the network, erasing system crashlogs and enabling ‘fcgi debugging’ which is used to log authentication attempts, including SSH logins. The ‘fcgi debugging’ option is not enabled by default and the Fortinet advisory recommends reviewing the setting as one possible indicator of compromise (IoC).
Historical Exploitation of Fortinet Devices
Fortinet vulnerabilities have historically been common targets for cyber attackers, and CVE-2025-32756 is the eighteenth Fortinet vulnerability to be added to the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency’s (CISA) Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) list.
| CVE | Description | Patched | Tenable Blog |
|---|---|---|---|
| CVE-2024-55591 | Fortinet Authentication Bypass in FortiOS and FortiProxy | January 2025 | CVE-2024-55591: Fortinet Authentication Bypass Zero-Day Vulnerability Exploited in the Wild |
| CVE-2024-21762 | Fortinet FortiOS Out-of-bound Write Vulnerability in sslvpnd | February 2024 | CVE-2024-21762: Critical Fortinet FortiOS Out-of-Bound Write SSL VPN Vulnerability |
| CVE-2023-27997 | FortiOS and FortiProxy Heap-Based Buffer Overflow Vulnerability | June 2023 | CVE-2023-27997: Heap-Based Buffer Overflow in Fortinet FortiOS and FortiProxy SSL-VPN (XORtigate) |
| CVE-2022-42475 | FortiOS and FortiProxy Heap-Based Buffer Overflow Vulnerability | December 2022 | CVE-2022-42475: Fortinet Patches Zero Day in FortiOS SSL VPNsAA23-250A: Multiple Nation-State Threat Actors Exploit CVE-2022-47966 and CVE-2022-42475 |
| CVE-2022-40684 | FortiOS and FortiProxy Authentication Bypass Vulnerability | October 2022 | CVE-2022-40684: Critical Authentication Bypass in FortiOS and FortiProxy |
Proof of concept
At the time of writing this, no proof-of-concept (PoC) has been published for CVE-2025-32756. When a PoC is released, we expect attackers will incorporate this vulnerability in their attacks as Fortinet devices have been exploited by threat actors, including nation-state actors in the past.
Vendor response
Fortinet has provided a list of IoCs based on their observations of CVE-2025-32756. We recommend reviewing the list of IoCs and steps recommended by Fortinet to determine if your device may have been impacted.
Solution
The following table details the affected and fixed versions of Fortinet devices affected by CVE-2025-32756:
| Product | Affected Version | Fixed Version |
|---|---|---|
| FortiCamera 2.1 | 2.1.0 through 2.1.3 | 2.1.4 or above |
| FortiCamera 2.0 | 2.0 all versions | Migrate to a fixed release |
| FortiCamera 1.1 | 1.1 all versions | Migrate to a fixed release |
| FortiMail 7.6 | 7.6.0 through 7.6.2 | 7.6.3 or above |
| FortiMail 7.4 | 7.4.0 through 7.4.4 | 7.4.5 or above |
| FortiMail 7.2 | 7.2.0 through 7.2.7 | 7.2.8 or above |
| FortiMail 7.0 | 7.0.0 through 7.0.8 | 7.0.9 or above |
| FortiNDR 7.6 | 7.6.0 | 7.6.1 or above |
| FortiNDR 7.4 | 7.4.0 through 7.4.7 | 7.4.8 or above |
| FortiNDR 7.2 | 7.2.0 through 7.2.4 | 7.2.5 or above |
| FortiNDR 7.1 | 7.1 all versions | Migrate to a fixed release |
| FortiNDR 7.0 | 7.0.0 through 7.0.6 | 7.0.7 or above |
| FortiNDR 1.5 | 1.5 all versions | Migrate to a fixed release |
| FortiNDR 1.4 | 1.4 all versions | Migrate to a fixed release |
| FortiNDR 1.3 | 1.3 all versions | Migrate to a fixed release |
| FortiNDR 1.2 | 1.2 all versions | Migrate to a fixed release |
| FortiNDR 1.1 | 1.1 all versions | Migrate to a fixed release |
| FortiRecorder 7.2 | 7.2.0 through 7.2.3 | 7.2.4 or above |
| FortiRecorder 7.0 | 7.0.0 through 7.0.5 | 7.0.6 or above |
| FortiRecorder 6.4 | 6.4.0 through 6.4.5 | 6.4.6 or above |
| FortiVoice 7.2 | 7.2.0 | 7.2.1 or above |
| FortiVoice 7.0 | 7.0.0 through 7.0.6 | 7.0.7 or above |
| FortiVoice 6.4 | 6.4.0 through 6.4.10 | 6.4.11 or above |
For users that are not able to immediately upgrade, Fortinet has provided a mitigation step; disabling the HTTP/HTTPS administrative interface. We recommend reviewing the Fortinet advisory for the latest information on workarounds and patched versions.
Identifying affected systems
A list of Tenable plugins for this vulnerability can be found on the individual CVE page for CVE-2025-32756 as they’re released. This link will display all available plugins for this vulnerability, including upcoming plugins in our Plugins Pipeline.
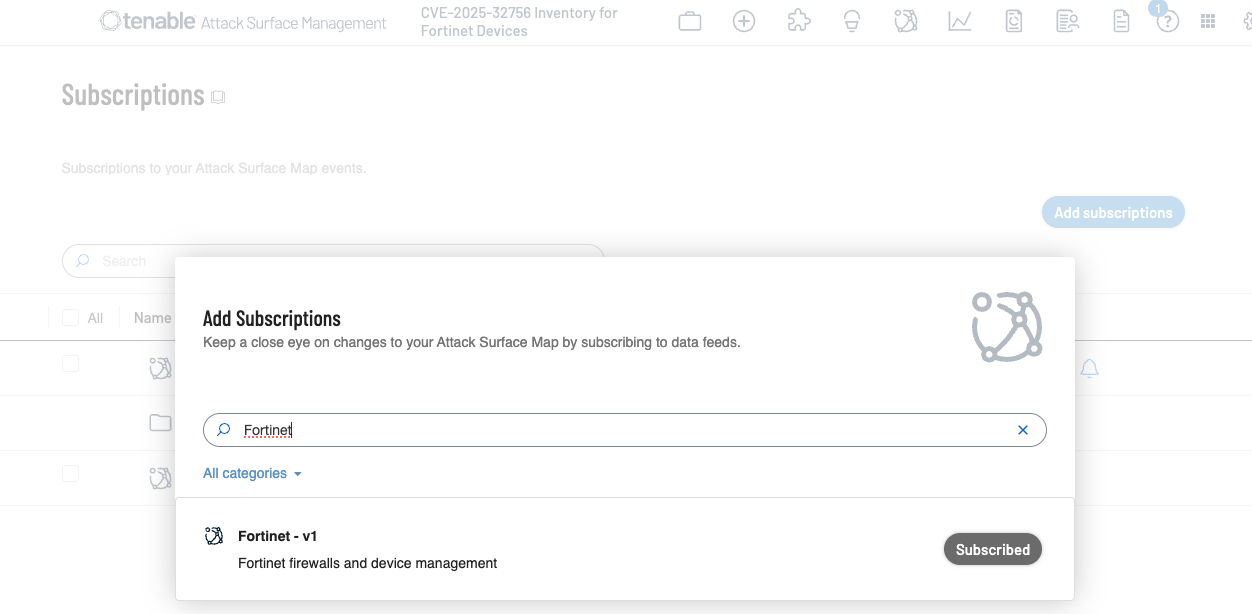
Additionally, customers can utilize Tenable Attack Surface Management to identify public facing assets running Fortinet devices by using the following subscription:
Get more information
Join Tenable's Security Response Team on the Tenable Community.
Learn more about Tenable One, the Exposure Management Platform for the modern attack surface.
- Exposure Management
- Vulnerability Management


