by Carole Fennelly
November 8, 2022
On November 3rd, 2021, Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) issued Binding Operational Directive (BOD) 22-01, Reducing the Significant Risk of Known Exploited Vulnerabilities, requiring federal agencies to identify and remediate a CISA managed catalog of known exploited vulnerabilities on their information systems. The National Cyber Awareness System (NCAS), is a system within CISA that produces advisories, alerts and situation reports, analysis reports, current activity updates, indicator bulletins, and more. On Jan 11, 2022 CISA issued an alert (AA22-011A) warning of increased risk to U.S. critical infrastructure. An additional alert was issued on Feb 16, 2022 (AA22-047A) warning of increased risks to U.S. Cleared Defense Contractors (CDCs) by Russian state-sponsored cyber attackers.
Tenable Vulnerability Management enables organizations to quickly summarize and track specific vulnerabilities to ensure proper discovery and mitigation. This dashboard showcases mitigation of these vulnerabilities to ensure a reduced attack surface in the organization.
CISA, the FBI, and NSA recommend that organizations apply the methods listed below for Identity and Access Management, Protective Controls and Architecture, and Vulnerability and Configuration Management:
- Require multi-factor authentication for all users, without exception
- Require accounts to have strong passwords, and do not allow passwords to be used across multiple accounts or stored on a system to which an adversary may have access
- Secure credentials
- Set a strong password policy for service accounts
- Audit Domain Controllers to log successful Kerberos TGS requests and ensure the events are monitored for anomalous activity
- Identify, detect, and investigate abnormal activity that may indicate lateral movement by a threat actor or malware
- Enable strong spam filters
- Update software, including operating systems, applications, and firmware on IT network assets, in a timely manner. Prioritize patching known exploited vulnerabilities, especially the CVEs identified in this CSA, and then critical and high vulnerabilities that allow for remote code execution or denial-of-service on internet-facing equipment
- Use industry recommended antivirus programs
- Disable all unnecessary ports and protocols
- Ensure OT hardware is in read-only mode
Tenable Vulnerability Management uses active credentialed scanning and/or agent-based scanning to collect information needed to identify known exploitable vulnerabilities. This information enables the risk manager to work with asset owners to establish an ongoing remediation action plan, which demonstrates compliance with this directive.
Risk-based vulnerability management (RBVM) is a process that reduces vulnerabilities across the agency's attack surface by prioritizing remediation actions to the risks CISA identifies. Tenable.io enables the agency to go beyond just discovering vulnerabilities and provides the life cycle steps to establish internal validation and enforcement procedures that demonstrate adherence with this directive.
Security leaders need to SEE everything, PREDICT what matters most and ACT to address cyber risk and effectively align cybersecurity initiatives with business objectives. Tenable.io discovers and analyzes assets continuously to provide an accurate and unified view of an organization’s security posture. The requirements for this dashboard are: Tenable Vulnerability Management (Nessus, NNM).
Widgets
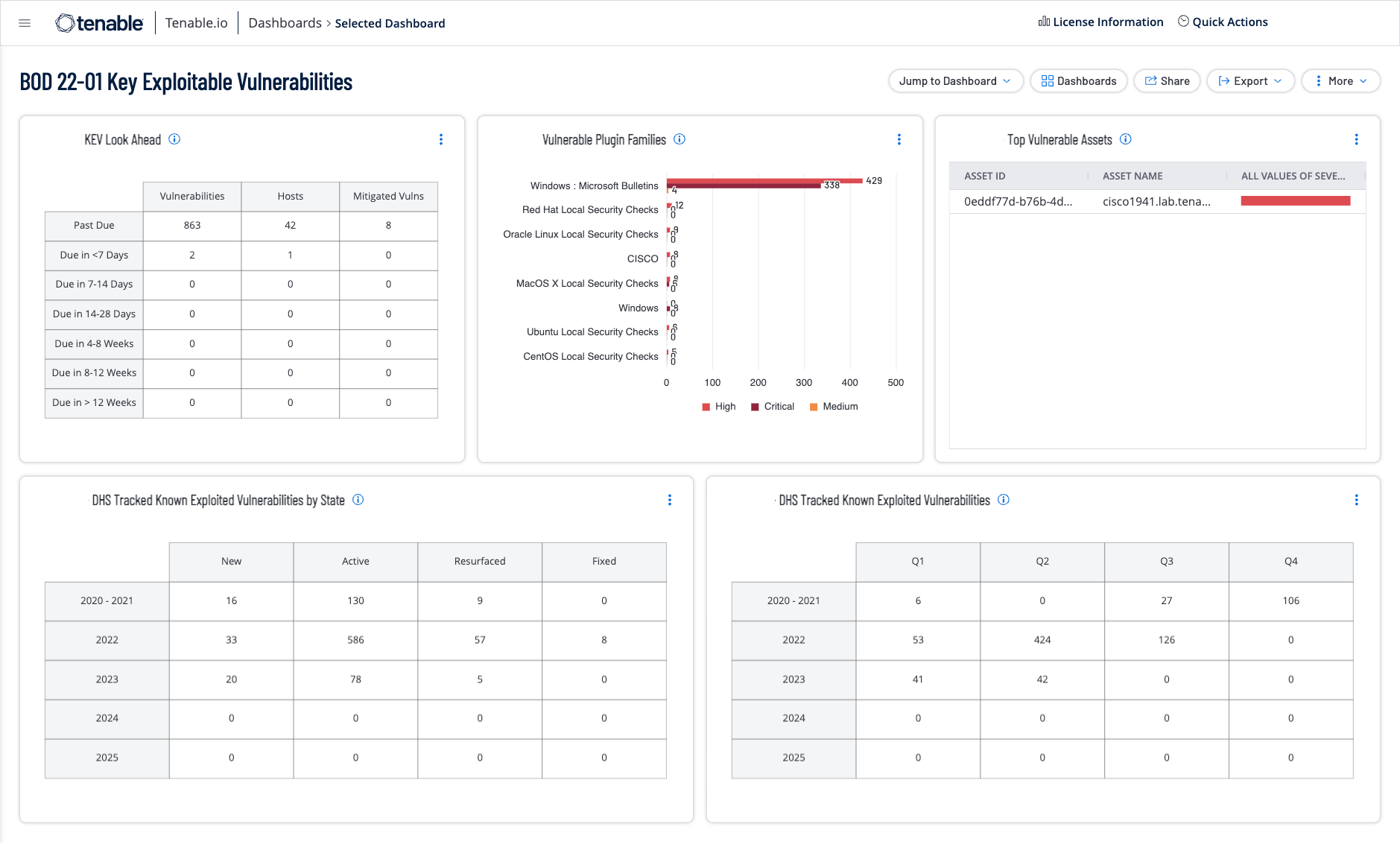
KEV Look Ahead: This widget displays a look ahead for DHS-tracked known vulnerabilities derived from the CISA Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog. This unique view presents a look at vulnerabilities that have imminent due dates. The forward view contains rows for vulnerabilities that are due to be fixed in the next 7 days, 7-14 days, 14-30 days, 30-60 days, 60-90 days, over 90 days out, and vulnerabilities that are past due for remediation.The requirements for this widget are: Tenable Vulnerability Management (Nessus).
Vulnerable Plugin Families: This widget displays vulnerability status counts for DHS tracked known vulnerabilities derived from the CISA Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog. The widget sorts vulnerabilities into known plugin families, displaying a count along with a bar graph of severity results. The requirements for this widget are: Tenable Vulnerability Management (Nessus).
Top Vulnerable Assets: This widget displays vulnerability status counts for DHS tracked known vulnerabilities derived from the CISA Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog. The widget displays the top most vulnerable assets The requirements for this widget are: Tenable Vulnerability Management (Nessus).
DHS Tracked Down Known Exploited Vulnerabilities by State: This widget displays vulnerability status counts for DHS tracked known vulnerabilities derived from the CISA Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog. The widget uses the CVE filter to exactly match the CVEs included in the CISA Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog and sorts the results in rows by year and state. The requirements for this widget are: Tenable Vulnerability Management (Nessus, NNM).
DHS Tracked Known Exploited Vulnerabilities: This widget displays vulnerability status counts for DHS tracked known vulnerabilities derived from the CISA Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog. The widget uses the CVE filter to exactly match the CVEs included in the CISA Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog and sorts the results in rows by year ranges and the quarter. The requirements for this widget are: Tenable Vulnerability Management (Nessus, NNM).