by Cesar Navas
October 12, 2016
New vulnerabilities are constantly being discovered in production software. Malicious attackers can make use of these vulnerabilities to infiltrate the network and steal or destroy critical information. Software on the network must be patched and updated to address these vulnerabilities, improving overall security and lowering risk for an organization. Patch management tools can be effective, but these tools may not be able to address all vulnerabilities on systems deployed within the enterprise. Manual patching yields inconsistent results, as many transient systems and devices connect to the network only periodically and may miss critical patches and updates. By implementing a consistent patch management process, organizations can identify and mitigate vulnerabilities that could be potentially devastating in a timely manner.
The French Network and Information Security Agency (Agence nationale de sécurité des systèmes d’information or ANSSI) developed the "40 Essential Measures for a Healthy Network" to assist organizations in safeguarding the security of information systems within a network. Following these measures, or rules, for a healthy network will provide basic protection for an organization's critical data. ANSSI states that the majority of IT attacks that have involved ANSSI stepping in could have been prevented had the IT measures set out in the guide been applied.
This dashboard aligns with Section III of the ANSSI 40 Essential Measures for a Healthy Network guide: Upgrade Software. This section contains two rules:
- Rule 6 focuses on identifying how software is being updated and keeping up to date on software patches. Organizations should prioritize core software components such as operating systems, office suites, browsers, and browser tools first. Downloading patches from trusted publishers helps to ensure that updates are obtained from reliable sources.
- Rule 7 addresses the need to define and apply a comprehensive update policy across all network assets. Dedicated patch management tools should be used to apply patches uniformly across the entire network. This rule recommends testing patches within an isolated environment before deploying them onto production systems, as this will help to ensure that critical systems are not adversely affected. Isolated devices that are not connected to the network must not be excluded from the update policy.
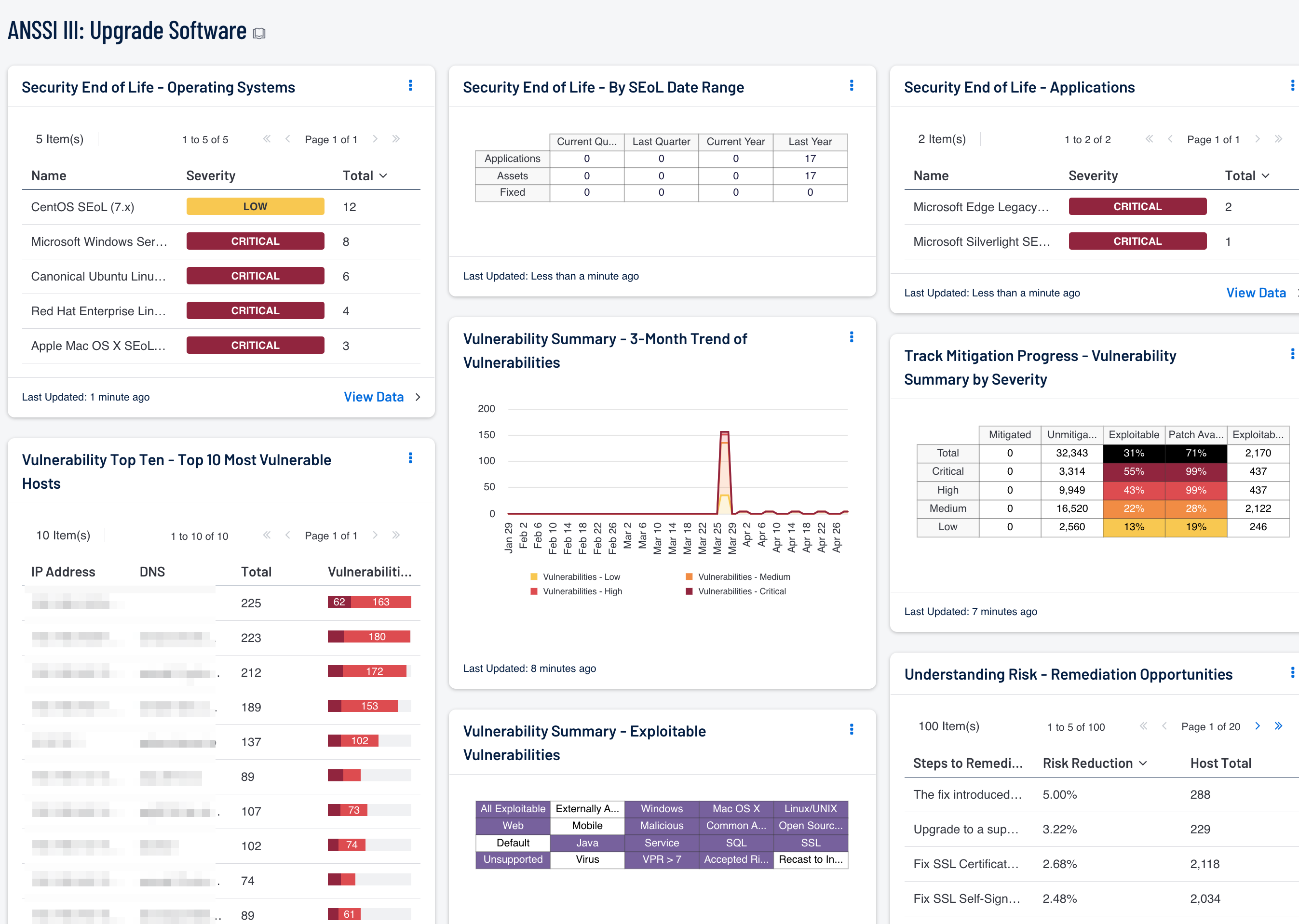
This dashboard provides a comprehensive view of existing vulnerabilities, vulnerability mitigation progress, and patch management events across the network. This information will assist an organization in better patching and updating the software on network systems, and ultimately safeguarding critical assets and data.
Components on this dashboard provide insight into the overall vulnerability of the network and the status of existing patch management efforts. Information on the most vulnerable hosts can assist security teams in addressing the greatest risks within the enterprise. Indicators for exploitable vulnerabilities highlight current vulnerabilities on the network that are known to be exploitable. An overview of remediation opportunities helps analysts quickly identify and prioritize those patches that do the most to reduce overall security risk. Monitoring patch management solutions provides valuable information that can assist in identifying systems that are not being patched due to errors or misconfigurations. Analysts can use the components within this dashboard to prioritize patch management efforts and apply patches to the most vulnerable hosts first. Vulnerability remediation progress is then tracked and reported by vulnerability severity.
This dashboard is available in the Security Center Feed, a comprehensive collection of dashboards, reports, Assurance Report Cards, and assets. The dashboard can be easily located in the Security Center Feed under the category Compliance & Configuration Assessment. The dashboard requirements are:
- Security Center 5.3.2
- Nessus 8.5.1
- NNM 5.9.1
Tenable's Security Center is the market-defining continuous network monitoring solution, and can assist an organization in managing the patching and updating of software. Security Center is continuously updated with information about advanced threats, zero-day vulnerabilities, and new regulatory compliance data. Active scanning periodically examines hosts to determine vulnerabilities and compliance concerns. Agent scanning enables scanning and detection of vulnerabilities on transient devices. Passive listening collects data to continuously monitor traffic and discover additional vulnerabilities. Host data and data from other security solutions is analyzed and correlated to monitor and report on patch management activity. Security Center provides an organization with the most comprehensive view of the network and network patch management, in order to safeguard critical assets and information.
The following components are included in this dashboard:
- Security End of Life - By SEoL Date Range - The Security End of Life Summary matrix displays the count of applications that are no longer supported by vendors, assets with unsupported applications, and mitigated assurances of the unsupported applications over different time periods.
- Security End of Life - Operating Systems - The Security End of Life - Operating Systems table displays all SEoL operating systems, associated severity, sorted by count.
- Security End of Life - Applications - The Security End of Life - Applications table displays all SEoL applications, associated severity, and is sorted by count.
- Vulnerability Summary - 3-Month Trend of Vulnerabilities: This component is a 3-month summary chart tracking unmitigated vulnerabilities of low, medium, high, and critical severity.
- Vulnerability Top Ten - Top 10 Most Vulnerable Hosts: This component shows the top ten hosts with exploitable vulnerabilities of high or critical severity.
- Understanding Risk - Remediation Opportunities: This table displays the top remediations for the network.
- Vulnerability Summary - Exploitable Vulnerabilities: This matrix displays warning indicators for exploitable vulnerabilities actively and passively detected on the network.