See all your cloud security risks. Close exposures fast.
Gain unmatched risk context—from your full cloud stack—to protect multi-cloud and hybrid cloud environments
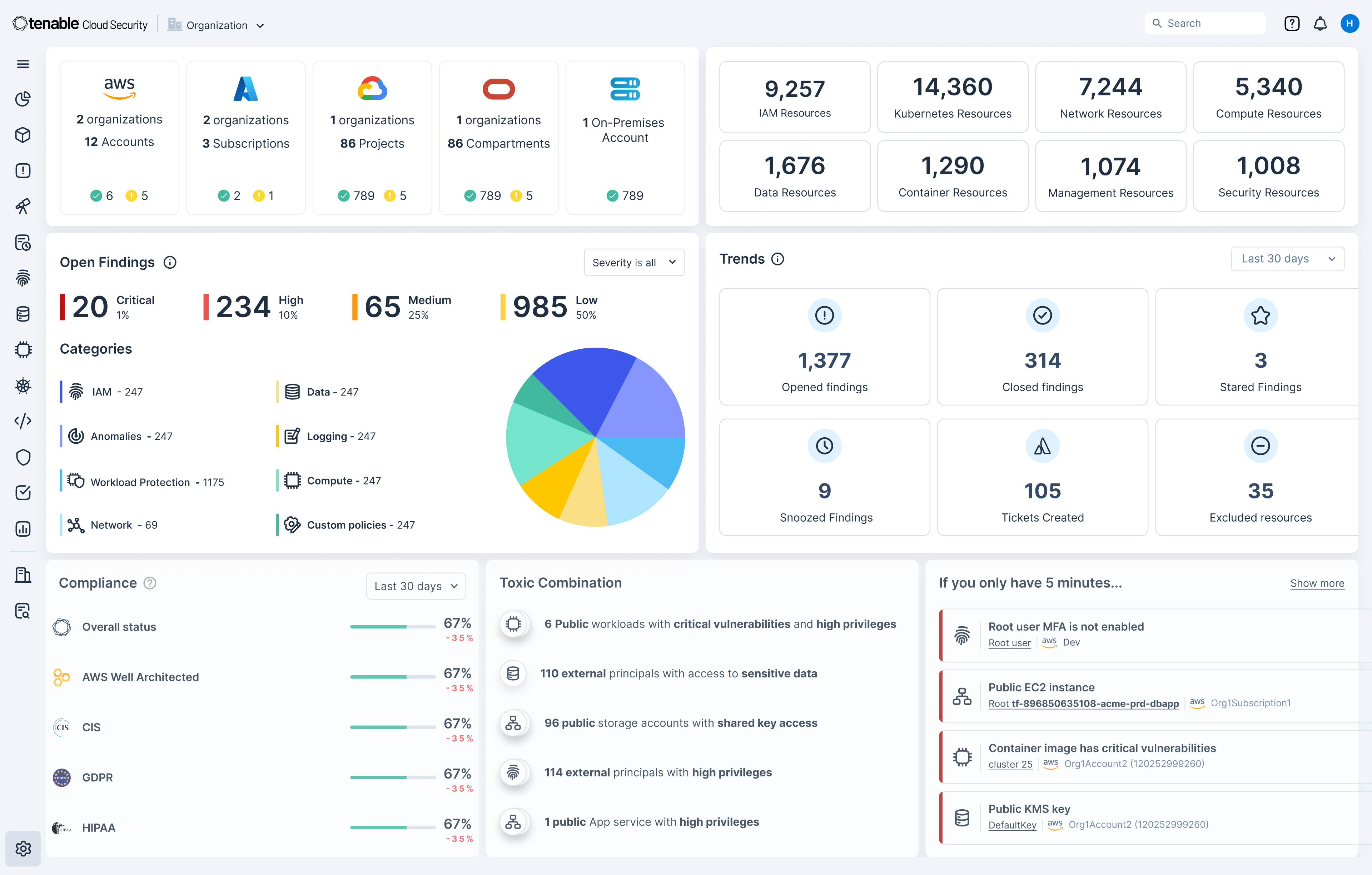
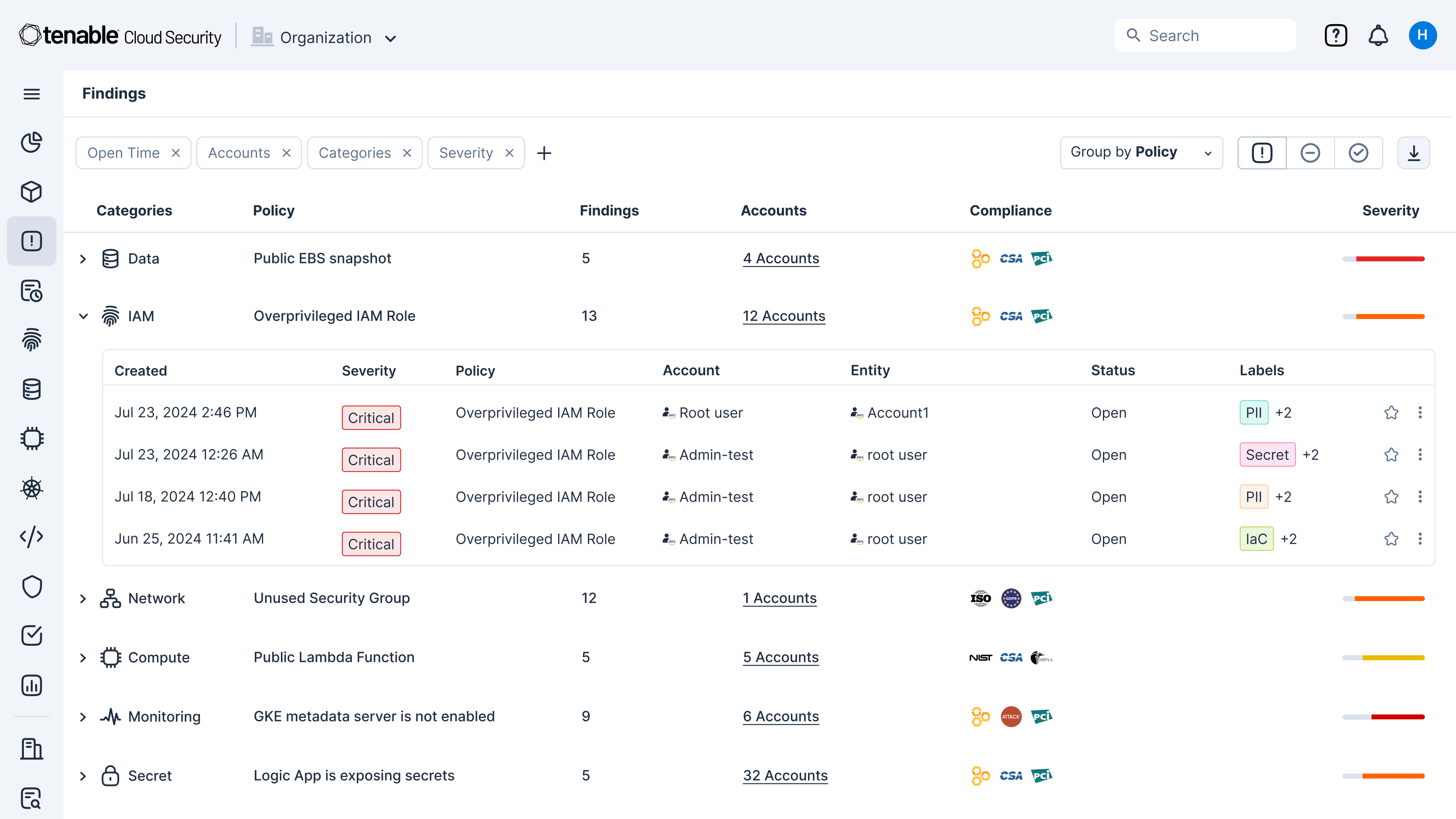
Quickly identify cloud exposures with full context
Secure your cloud from the four big risks: misconfigurations, vulnerabilities, unsecured identities and vulnerable sensitive data. Expose toxic combinations of these risks to prioritize critical remediation steps.
Unify visibility for multi-cloud resources
Get a unified inventory of all your cloud assets. From development to runtime, continuously discover resources across your cloud and hybrid environments including infrastructure, workloads, AI resources, identities, containers, Kubernetes and infrastructure as code (IaC).
Gain a 360-degree view of risk
Use integrated cloud security tools to find vulnerabilities, misconfigurations and excessive permissions across your cloud environments. Use Tenable’s Vulnerability Priority Rating scores to focus on the critical risks across your multi-cloud and on-prem attack surface. Prioritize risks that matter most while enforcing the principles of zero trust and least privilege, including through just-in-time (JIT) access.
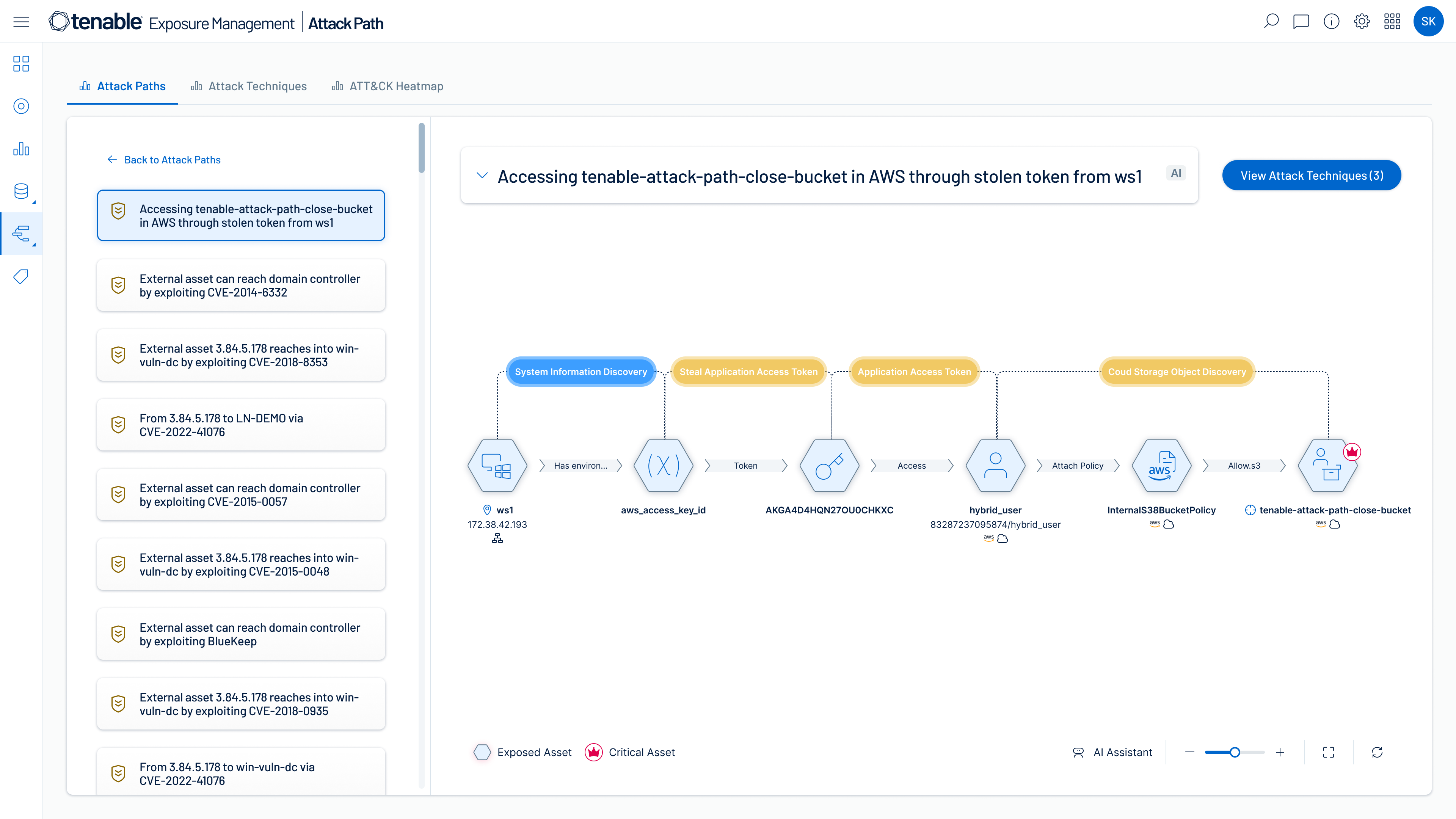
Identify high-risk attack paths
Map complex asset, identity and risk relationships to uncover attack paths that traverse hybrid cloud environments. Prioritize remediation of choke points that disrupt attack paths before breaches begin.
Find, prioritize and reduce cloud security risks with accuracy and confidence
When you choose Tenable Cloud Security as part of the Tenable One Exposure Management Platform — in addition to getting deep insight into all your cloud resources, identities and risks — you can extend exposure management to secure your entire attack surface including multi-cloud and hybrid cloud environments.
ExposureAI
Empower lightning-fast analysis and decision making with generative AI that streamlines discovery of hidden insights and deep security expertise.
Attack path analysis
Visualize complex asset, identity and risk relationships across security domains and prioritize remediation of true exposure before breaches happen.
Exposure View
Streamline measurement and communication of cyber exposure with business-aligned views that help you optimize decision making and investments.
Exposure graph
Act confidently with the world's largest repository of contextual asset, exposure and threat data that fuels Tenable ExposureAI's unparalleled insights.
Inventory
Gain a unified view of all your assets and risk across the attack surface: unseen assets, IT, OT, IOT, cloud, identities and applications.
Vulnerability intelligence
Access the most complete knowledgebase of vulnerability and threat insights from Tenable Research, NVD and other trusted sources in a single place.
Third-party data sources
Integrate and consolidate asset and risk data from your existing tools, and put it to work along side your trusted Tenable data.
Cloud exposure
Discover and prioritize remediation of cloud exposure across all your clouds, assets and identities with the most actionable CNAPP.
Vulnerability exposure
Discover and prioritize remediation of vulnerability exposure across the modern attack surface with industry-leading vulnerability management.
OT exposure
Discover and prioritize remediation of operational exposure across your converged IT/OT/IoT environment.
Identity exposure
Discover and prioritize remediation of identity exposure across your Active Directory and Entra ID environments.
Tenable One
The AI-powered exposure management platform that unifies security visibility, insight and action across the attack surface.
Reduce common cloud vulnerabilities
The new Tenable Cloud Risk Report 2024 reveals a “toxic cloud trilogy” of vulnerabilities that are:
- Publicly exposed
- Critically vulnerable
- Highly privileged
Explore the report to learn how to tackle these vulnerabilities and mature your cloud security strategy by evolving from vulnerability management to comprehensive exposure management. With Tenable Cloud Security, you can better prioritize and reduce risk by gaining context from across your cloud stack including cloud identity issues, vulnerability exposures, misconfigurations and data risks — all in a single platform.
Read the reportEliminate cloud blind spots with advanced exposure management capabilities
Learn more about Tenable Cloud Security
Using [Tenable Cloud Security] automation allowed us to eliminate exhaustive manual processes and perform in minutes what would have taken two or three security people months to accomplish.
- Tenable Cloud Security
 AWS
AWS Azure
Azure Google Cloud
Google Cloud